(OSA): Symptoms, Treatments, and Causes
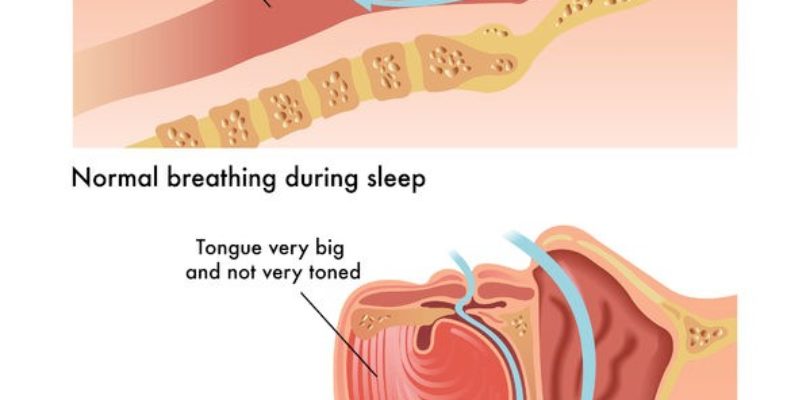
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a respiratory seizing caused by the collapse of the walls of the pharynx. The disorder mainly occurs while the person is asleep and snoring. To be more exact, during the attack, a patient stops snoring because of the blockage of the air passage through the pharynx. Repeated episodes of obstructive sleep apnea result in the lowest blood oxygenation, which may result in damage to the body.
In adults, the main features of the disorder are: 1) suspension of breathing for 10 seconds in five or more episodes per hour of sleep, 2) reduction of oxygen levels in the blood. In children, it only takes 2 or 3 seconds of respiratory arrest for blood.
Obstructive sleep apnea mostly affects middle-aged obese men. The disease can cause or worsen the cases of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, arrhythmias, heart attacks and congestive heart failure.
Aggravating factors
Some factors which contribute to the onset of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea are:
- Tonsils and very large adenoids;
- Obstruction chronic nose because of tumors, deviated septum, nasal polyps and hypertrophy of the turbinate;
- Sleeping up belly;
- Alcohol, tobacco, drugs based on benzodiazepines and gastroesophageal reflux;
- Obesity, because it favors the fat infiltration in pharynx
The synergism between these factors enhances the tendency to narrowing of the pharynx and apnea.
Symptoms
There are various common symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea: snoring, restless sleep, lack of energy and daytime sleepiness. Apart from these, headache, disturbance of memory, attention and concentration, prone to depression, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, and especially numerous arousals are also some of the less frequent symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea. The patient suffering, wakes up with confusion, because of the effort he/she spends breathing and hypoxemia. The effort in breathing alerts the brain about the lack of oxygen.
What problems can occur with sleep apnea untreated?
Sleep apnea can affect the quality of life along with the peaceful sleep. Untreated, sleep apnea can cause serious problems sooner or later. Some people can get affected in terms of healing and growth. Sleep apnea can also worsen other health conditions. Over time, sleep apnea can increase blood pressure (hypertension) and increase the risk of heart disease and eventually may cause death.
Treatment
The treatment is always multidisciplinary and varies with the severity of the case. The first therapeutic approach is to try to reduce the aggravating factors of OSAS. Therefore, the patient must:
- Tackle the causes of nasal obstruction and gastroesophageal reflux;
- Lose weight;
- Avoid the use of alcohol, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants and a cigarette a few hours before bedtime.
If these measures are not enough, you can also make use of the use oral prostheses that prevent the fall of the tongue backward. The CPAP and special masks can also be used which maintain continuous positive pressure on the airways, preventing clogging. There are situations, however, where surgery or cauterizations are necessary to cure the elements that generate the obstruction, such as those related to changes in the tonsils and adenoids.
Recommendations
The adoption of simple measures can help you sleep better and avoid apnea attacks. Here are some examples:
- Try to establish and follow the hours of bedtime and rise;
- Avoid drinking substances containing caffeine;
- Do not smoke in at least 4 or 5 hours prior to the time of going to bed;
- Do not overdo the use of alcohol, or make heavy meals before bedtime.